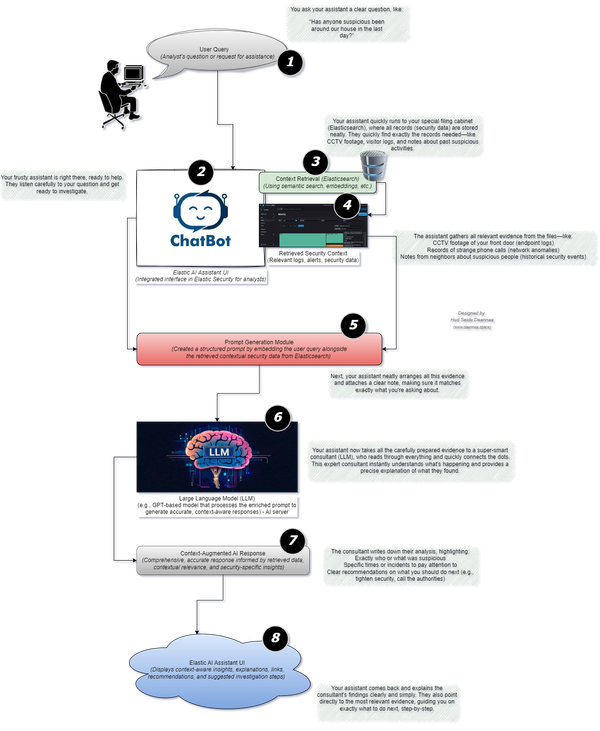
Integrating Cyber Threat Intelligence for Business-Driven Security Operations
This framework shows how CTI enhances security by aligning with business objectives. It covers governance, asset categorization, and SOC operations, enabling proactive threat response through strategic, operational, and tactical intelligence.

This diagram illustrates the critical role of Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) within an organization's cybersecurity framework. It highlights how CTI empowers security by helping businesses understand and counter threats effectively, aligning security actions with business objectives. Governance, asset categorization, and threat modeling form the core, leading to policies and controls in the SOC. Red and Blue teams leverage CTI for offensive and defensive operations, while strategic, operational, tactical, and technical intelligence cycles refine responses. This proactive approach ensures adaptive, business-aligned security resilience.
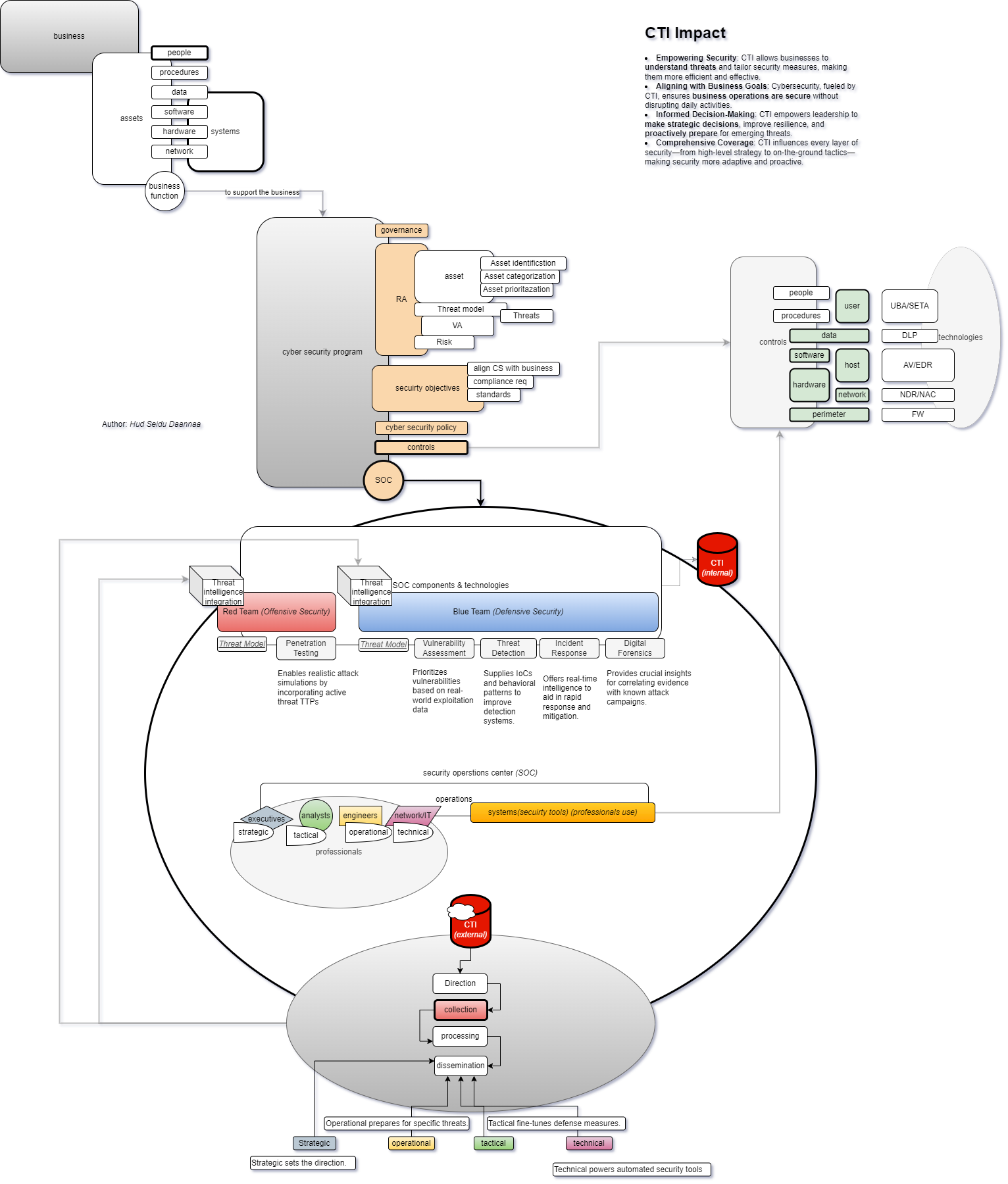
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is not just a tool for detecting threats but a strategic asset that aligns cybersecurity with business needs. By identifying and categorizing assets, understanding threats, and prioritizing vulnerabilities, CTI enables organizations to focus on protecting what matters most.
Red and Blue teams within the SOC utilize CTI insights to simulate realistic attacks (Red) and strengthen defenses (Blue). This structured approach integrates intelligence at four levels:
- Strategic: Aligns security objectives with business goals, ensuring executive buy-in.
- Operational: Provides actionable intelligence to prepare for specific threats.
- Tactical: Fine-tunes defenses based on current threat patterns.
- Technical: Powers automated tools, making security adaptive and efficient.
CTI’s comprehensive scope covers end-to-end security—from governing policies and threat modeling to incident response and forensic analysis—supporting a resilient and business-aligned cybersecurity posture.